Mr Aurand presented in detail the functions and activities of the OIV and the advantage for consumer countries, in particular, of being involved in the work and the scientific community of the Organisation.
The Korean Ambassador highlighted the increase in wine consumption in his country, noting the growing share of Asian countries in global wine trade. The Director General of the OIV said that the contact he had made in Seoul with the ministries responsible for food and agriculture had led to a constructive dialogue and hoped that the Embassy could be an information relay to Korean Foreign Affairs in order to advance the idea of joining the OIV.


This Act supplements chapter V, Part VI of Book VI of the Rural and Maritime Fishing Code by Section L. 665-6 that reads as follows:
"Sect. L. 665-6. - Wines, vine products, viticultural terroirs as well as ciders and perries, spirituous beverages and beers derived from local traditions are part of the protected cultural, gastronomic and landscape heritage of France. "
Following in the footsteps of Uruguay or Argentina, which recognised wine as the "national drink", France is thus recognising special protection for wine and viticultural terroirs by integrating them into France's cultural, gastronomic and landscape heritage. It should be noted that the gastronomic French meal has been inscribed on the UNESCO Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity since 2010. This is a festive meal during which guests practice, for the occasion, the art of "good eating and drinking".

H.E. Mr Lipka stressed the importance of this international recognition, which attracts a huge number of submissions every year from OIV Member Countries and non-Member Countries.
This prestigious international award enables a readership seeking quality works to find bibliographic references for everything to do with knowledge and popularisation of the vine and wine sector, as well as to discover scientific works of a very high standard.
The Director General of the OIV, Mr Jean-Marie Aurand, reminded those present that the 2014 award winners undoubtedly illustrate the OIV's decades-old vision of always being the world's reference organisation for vine and wine.

These recognitions contribute to the promotion of the image of viticulture throughout the world, and its different dimensions: scientific and technical, economic, cultural, even historic.
Finally, the President of the OIV Award Jury warmly congratulated the authors who won an award, as well as the publishers, for their cultural, technical or hedonistic contributions, each and every one of whose diverse approaches seeks to share a common passion for the vine and wine world.

Through analysis of the information available on manganese, the authors of the paper, V. D. Gómez-Miguel and V. Sotés, President of the OIV "Viticulture" Commission, provide a solid grounding on the issue of manganese in viticulture.
This work was presented during the OIV meetings in April 2014 as part of the consultation with the OIV Member States regarding the manganese content in soils, clusters, musts and wines; the impact of soils on the manganese migration to the plant; the impact of vinification techniques on manganese levels in wines; and additional information on the toxicity of manganese.
Download this publication (available in Spanish only)

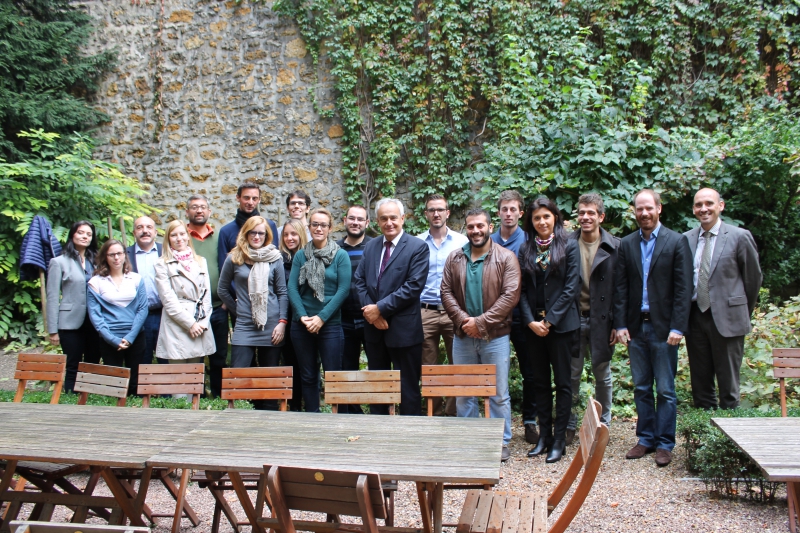
The 16 participants of 8 different nationalities in this year's class will meet more than 500 wine sector professionals in 24 producer and/or consumer countries across 5 continents.
On this occasion, the Director General of the OIV, Jean-Marie Aurand, emphasised the importance of the network created over 25 years ago by this training programme, both with regard to the graduates and universities as well as the companies involved in this unique approach. He also reminded those present of the relevance of this international training programme in relation to the increased globalisation of wine markets.
More information on the OIV MSc in Wine Management: www.oivmsc.org/en/.
