
Grapevine trunk diseases (GTD) have become a real problem during the last years.
OIV also, has started up again the work in this sense according to its Strategic plan and work program, which first action was settled down in 2006 (VITI 02/2006 resolution) but some actions are needed nowadays in order to complete this resolution about preventive measures.
It is important to underline that this topic is evaluated by several initiatives and actions developed at national or international level.
The OIV Secretariat general has wished to elaborate a document underlying the importance of this topic, the ongoing works and the need for an international cooperation.
Download document (in English)

During this meeting, the Codex Alimentarius Commission adopted several standards, some of which have a direct impact on the international vitivinicultural sector.
With regard to additives in wine (category 14.2.3), the Member States of the Codex Alimentarius approved the inclusion of carbon dioxide among those subject to GMPs, with the following note: “The CO2 content in finished still wine shall not exceed 4000 mg/kg at 20°C”.
Four additives, regarding the "Grape wines" category in particular, were added to the priority list of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee (JECFA) for toxicological assessment. These were, namely, tannins, yeast mannoproteins (INS 455), potassium bisulphite (INS 228) and metatartaric acid (INS 353).
Furthermore, the Commission adopted a number of Maximum Residue Limits for pesticides used in the production of table grapes or dried grapes.
The existing limits for these pesticides, listed below, were revoked and replaced by the following limits:
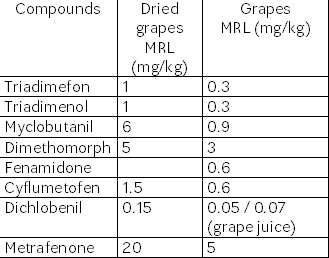
Note: With regard to MRLs, the OIV Secretariat has put together a list of online links on the website www.oiv.int. The list includes information available concerning maximum residue limits applicable to grapes (table, wine and dried grapes) and to wines (where relevant).
This information is based on:
- notifications from Member Countries, as requested in adopted OIV resolutions,
- notifications made by countries to the WTO,
- other sources: Codex Alimentarius, EU, the USDA MRL database.
The full report of the 38th session of the Codex Alimentarius may be viewed online at http://www.codexalimentarius.org/meetings-reports. The next Codex Alimentarius Commission session will take place from 27 June to 1 July 2016.